sumtyme.ai
Developer Hub
A Python interface for interacting with the Embedded Intelligence Platform (EIP). The EIP uses a proprietary AI architecture called Abstract Generalised Networks (AGNs) to model how complex systems evolve.
Unlike traditional machine learning, AGNs do not require training data, fine-tuning, or retraining. Instead, they autonomously rewrite their underlying algorithms as they observe new data, allowing them to holistically understand how directional shifts influence a system. This approach is ideal for analyzing dynamic domains like financial markets and weather patterns, focusing on the structure of change rather than just predicting the next step.
Explainers
AGNs vs. Traditional Architectures
AGNs vs. Traditional Architectures
Traditional AI architectures often struggle to model complex, dynamic systems because they’re limited to predicting the next step in a sequence using fixed, linear patterns.Abstract Generalised Networks (AGNs), on the other hand, provide a more robust understanding by modelling the underlying abstract structure of a time series using category theory. This allows them to grasp the complex dynamics that cause changes in an environment.AGNs are not autoregressive and analyse the entire data window simultaneously. Therefore, any outputs observed before the last data period of a window should be used for context and not as a prediction. The recommended window size is 5001 data periods.
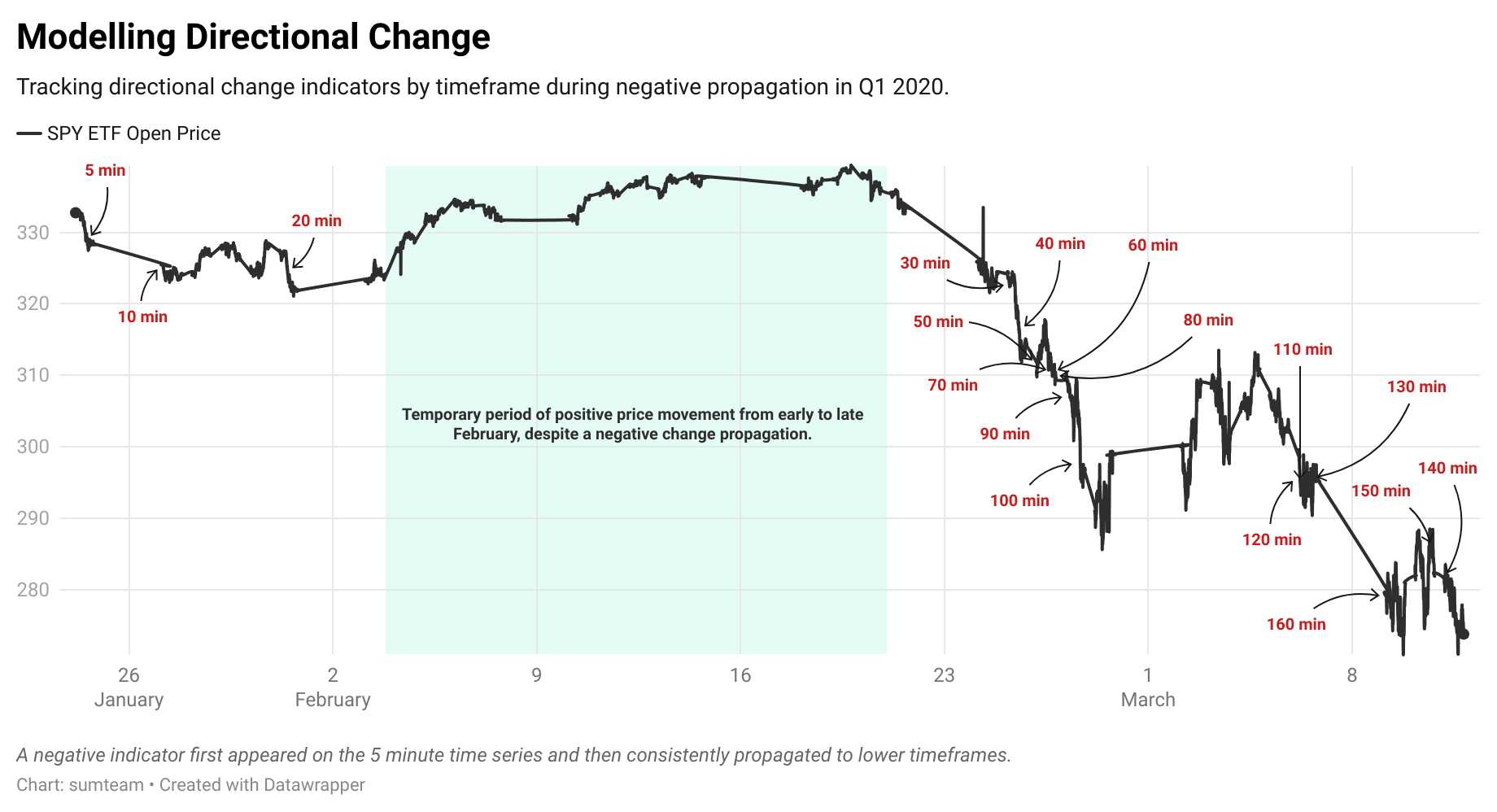
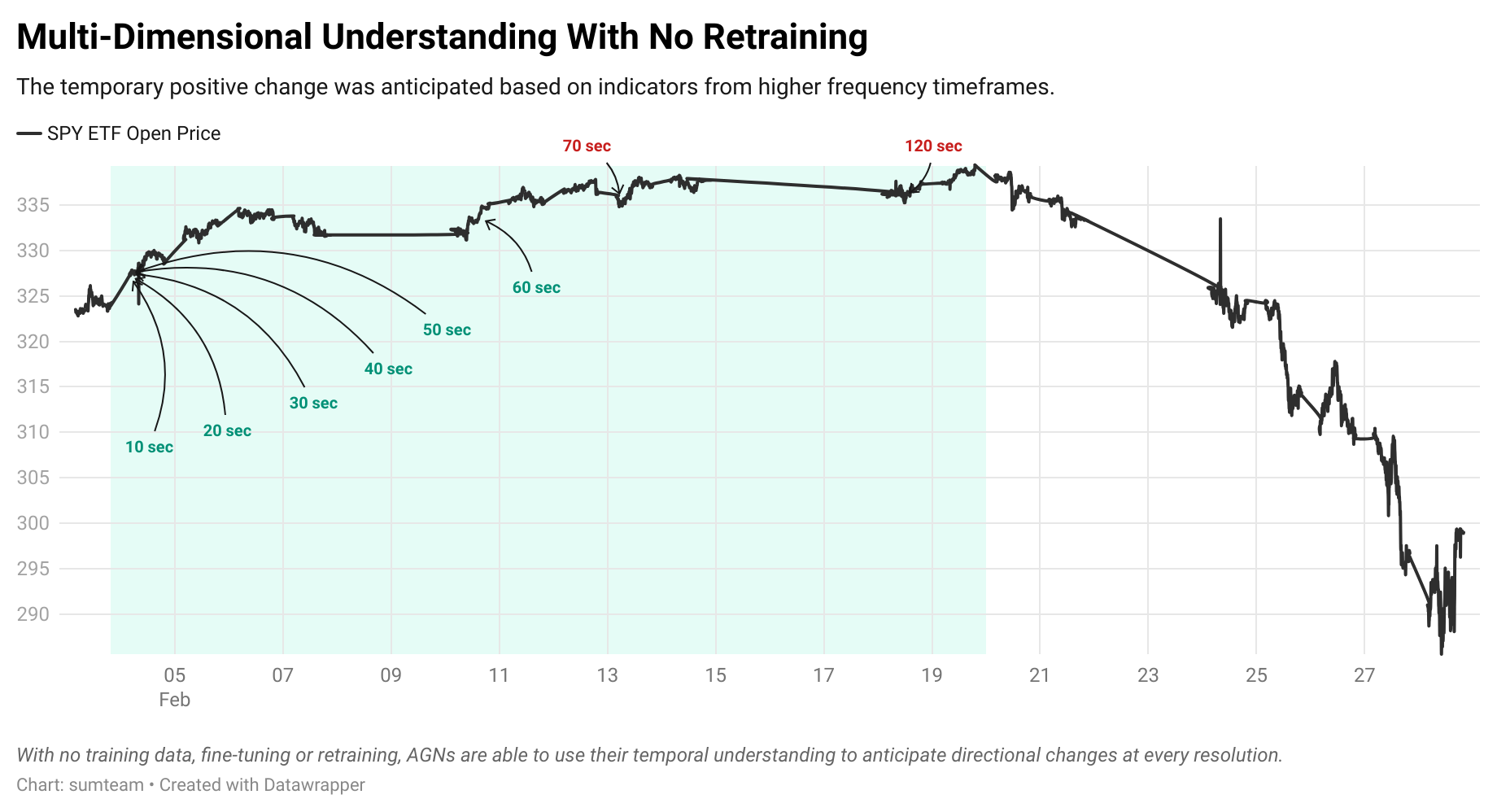
Information Propagation
Information Propagation
Abstract Generalised Networks (AGNs) operate on the theory of information propagation across timeframes. When a directional change is identified on a high-frequency timeframe, it creates an early indicator. As this move evolves, that indicator propagates to lower-frequency timeframes reinforcing the earlier indicator. This propagation continues until the move is fully developed and the indicator dissipates. This provides a deeper understanding of a system’s evolution that moves beyond a simple next-step prediction.
Demonstrations


Python Quickstart - Finance
Model Environment
Analyses the environment to forecast a directional change for the final period.
Forecast Change
Forecasts a directional change for the final period.
Rolling Forecast
Performs a rolling analysis to identify evolving trends.

